The element potassium's atomic number is 19. Its relative atomic mass is 39.098. How many protons occur in a potassium atom?
1 Answer
Well, a neutral atom's atomic number is equal to the number of protons and electons it has. Therefore protons=19 and electons=19 since potassium's atomic number is 19. The number of neturons an atom has is derived from mass number minus the number protons. So, neutrons=20 since 39 (mass#)-19 (# of protons)=20. Potassium is an alkali metal in group IA of the periodic table with atomic number 19, an atomic weight of 39.102, and a density of 0.86 Mg/m 3. Its melting point is 63.7 C, and it boils at 760 C. The electronic configuration of Potassium is (Ar) (4s 1). Its atomic radius is.
Explanation:
- Assume the potassium density ρ = 860 kg/m 3 and atomic mass A = 39.1 ×10 –3 kg/mol.
- 2020-11-21 by Nick Connor Atomic Mass of Potassium Atomic mass of Potassium is 39.0983 u.
This is a perfect example of a problem that wants to test your understanding of a basic concept.
Atomic No Of Potassium Nitrate

An element's atomic number tells you how many protons are present inside that element's nucleus. As you can see, the answer is given away in the question, provided that you know what the atomic number is all about.
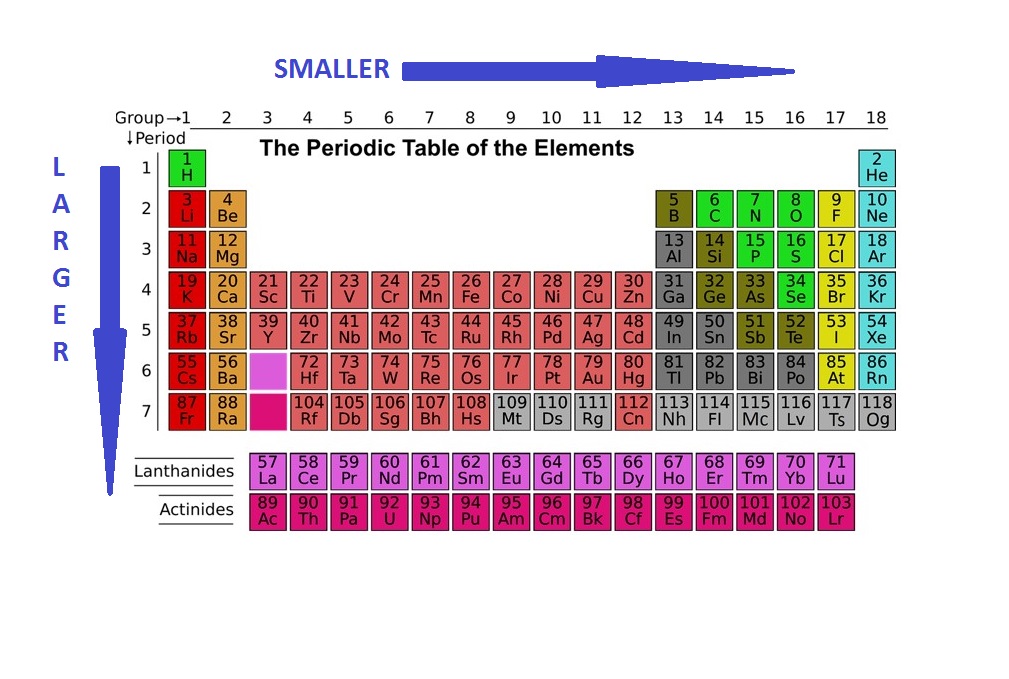
You can thus say that an atom of potassium contains
You can use the relative atomic mass,
To do that, simply take the value of the relative atomic mass and round it to the nearest integer. This will get you the mass number of the most abundant potassium isotope.
In your case, you have
Atomic No. Of Potassium
This tells you that the most abundant isotope of potassium contains
You now know that the most abundant isotope of potassium contains
Related questions
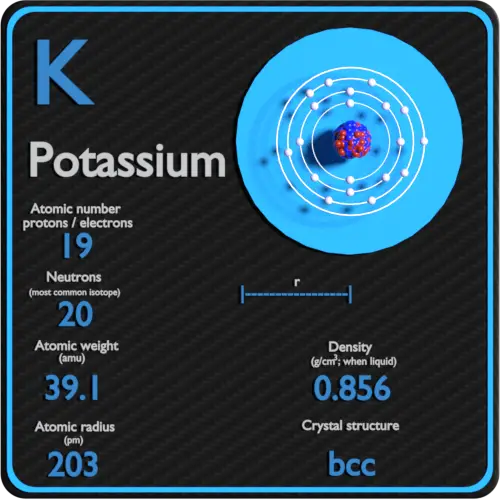
| Potassium metal is silvery grey |
Potassium
| Atomic Number: | 19 | Atomic Radius: | 275 pm (Van der Waals) |
| Atomic Symbol: | K | Melting Point: | 65.5 °C |
| Atomic Weight: | 39.10 | Boiling Point: | 759 °C |
| Electron Configuration: | [Ar]4s1 | Oxidation States: | +1, −1 (a strongly basic oxide) |
History
From the English word, potash - pot ashes; Latin kalium, Arab qali, alkali. Discovered in 1807 by Davy, who obtained it from caustic potash (KOH); this was the first metal isolated by electrolysis.
Sources
The metal is the seventh most abundant and makes up about 2.4% by weight of the earth's crust. Most potassium minerals are insoluble and the metal is obtained from them only with great difficulty.
Certain minerals, however, such as sylvite, carnallite, langbeinite, and polyhalite are found in ancient lake and sea beds and form rather extensive deposits from which potassium and its salts can readily be obtained. Potash is mined in Germany, New Mexico, California, Utah, and elsewhere. Large deposits of potash, found at a depth of some 3000 ft in Saskatchewan, promise to be important in coming years.
Potassium is also found in the ocean, but is present only in relatively small amounts, compared to sodium.
Production
What Is The Atomic No. Of Potassium
Potassium is never found free in nature, but is obtained by electrolysis of the hydroxide, much in the same manner as prepared by Davy's first process. Thermal methods also are commonly used to produce potassium (such as by reduction of potassium compounds with CaC2, C, Si, or Na).
Uses
The greatest demand for potash has been in its use for fertilizers. Potassium is an essential constituent for plant growth and is found in most soils.
An alloy of sodium and potassium (NaK) is used as a heat-transfer medium. Many potassium salts are of utmost importance, including the hydroxide, nitrate, carbonate, chloride, chlorate, bromide, iodide, cyanide, sulfate, chromate, and dichromate.
Properties
It is one of the most reactive and electropositive of metals. Except for lithium, it is the lightest known metal. It is soft, easily cut with a knife, and is silvery in appearance immediately after a fresh surface is exposed. It rapidly oxidizes in air and must be preserved in a mineral oil such as kerosene.
Potassium Atomic Mass
As with other metals of the alkali group, it decomposes in water with the evolution of hydrogen. It catches fire spontaneously on water. Potassium and its salts impart a violet color to flames.
Atomic No Of Potassium Carbonate
Potassium Atomic Radius
Isotopes
Seventeen isotopes of potassium are known. Ordinary potassium is composed of three isotopes, one of which is 40°K (0.0118%), a radioactive isotope with a half-life of 1.28 x 109 years.
Handling
The radioactivity presents no appreciable hazard.

Comments are closed.